 |
| Hemiparesis |
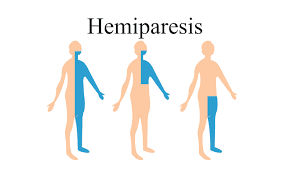
What is Hemiparesis?
Hemiparesis is a medical condition that results in weakness or paralysis on one side of the body. It is usually caused by damage to the part of the brain that controls movement, such as a stroke or a traumatic brain injury. Hemiparesis can affect various parts of the body on one side, including the face, arm, and leg.
The severity of hemiparesis can vary depending on the extent and location of the brain damage. In some cases, it may only cause mild weakness or difficulty with movement, while in other cases it can result in complete paralysis of one side of the body.
Treatment for hemiparesis may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, medication, and other interventions to help improve mobility and function. The goal of treatment is to help the individual regain as much function as possible and improve their quality of life.
What are the causes of Hemiparesis?
Hemiparesis can be caused by a variety of medical conditions that result in damage to the brain or nervous system. Some of the most common causes of hemiparesis include:
Stroke: A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted, which can result in brain damage and hemiparesis.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI): A TBI occurs when there is a sudden impact to the head, such as in a car accident or fall, which can result in brain damage and hemiparesis.
Brain tumor: A tumor in the brain can cause pressure and damage to the surrounding tissue, which can result in hemiparesis.
Multiple sclerosis (MS): MS is a disease that affects the nervous system and can cause hemiparesis, among other symptoms.
Cerebral palsy: Cerebral palsy is a condition that affects movement and muscle tone and can cause hemiparesis in some cases.
Infections: Certain infections, such as encephalitis or meningitis, can cause inflammation and damage to the brain, which can result in hemiparesis.
Congenital brain abnormalities: Some individuals may be born with brain abnormalities that can cause hemiparesis, such as cerebral malformations or hydrocephalus.
The specific cause of hemiparesis can vary depending on the individual and their medical history. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of hemiparesis.
What are the symptoms of Hemiparesis?
The symptoms of hemiparesis can vary depending on the extent and location of the brain damage, but typically involve weakness or paralysis on one side of the body. Some of the most common symptoms of hemiparesis include:
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, which can affect the face, arm, and leg
- Difficulty with movement or coordination on one side of the body, such as difficulty walking or performing daily activities
- Loss of sensation or feeling on one side of the body
- Changes in vision or speech, such as slurred speech or difficulty understanding language
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Muscular stiffness or spasticity on one side of the body
- Fatigue or decreased endurance when using the affected limb or side of the body
The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the extent of the brain damage and the underlying cause of the hemiparesis. It is important to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can help improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
What is the difference between Hemiplegia and Hemiparesis?
Hemiplegia and hemiparesis are both conditions that affect one side of the body, but they are different in terms of the extent of the paralysis or weakness.
Hemiplegia refers to complete paralysis on one side of the body, including the arm, leg, and trunk. This means that the affected individual has no movement or sensation on one side of their body.
Hemiparesis, on the other hand, refers to weakness or partial paralysis on one side of the body. This means that the affected individual may have some movement or sensation on one side of their body, but it is limited or impaired.
Both hemiplegia and hemiparesis are typically caused by neurological conditions, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or brain tumors. The treatment for both conditions typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, medication, and other interventions to help improve mobility and function.
In summary, hemiplegia and hemiparesis are both conditions that affect one side of the body, but hemiplegia refers to complete paralysis while hemiparesis refers to weakness or partial paralysis.
How to Diagnose Hemiparesis?
Hemiparesis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The process may involve the following steps:
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any other relevant information to help identify possible causes of hemiparesis.
- Physical examination: Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess your strength, coordination, and reflexes, as well as check for any other neurological symptoms.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, may be ordered to help identify any damage or abnormalities in the brain that may be causing hemiparesis.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to help identify underlying conditions or infections that may be causing hemiparesis.
- Electromyography (EMG): An EMG may be used to evaluate the electrical activity of your muscles and nerves to help diagnose the cause of your symptoms.
- Other tests: Your healthcare provider may order additional tests, such as a lumbar puncture or electroencephalogram (EEG), depending on your specific symptoms and medical history.
The specific diagnostic process will vary depending on the individual and their symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of hemiparesis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
Treatment of Hemiparesis
The treatment of hemiparesis typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, medication, and other interventions to help improve mobility and function. The goal of treatment is to help the individual regain as much function as possible and improve their quality of life.
Some of the most common treatments for hemiparesis include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy involves exercises and activities to help improve strength, flexibility, and coordination. This may include exercises for the affected limb or side of the body, as well as exercises to help improve balance and mobility.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy focuses on improving the individual's ability to perform daily activities, such as dressing, bathing, and eating. This may involve the use of adaptive devices or modifications to the individual's environment.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of hemiparesis, such as muscle stiffness or spasticity. These may include muscle relaxants or anti-spasticity medications.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat the underlying cause of hemiparesis, such as a brain tumor or blood clot.
- Other interventions: Other interventions, such as speech therapy or assistive technology, may also be used to help improve communication and function.
The specific treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause of hemiparesis, as well as the individual's symptoms and overall health. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the individual's specific needs and goals.
Physiotherapy treatment in Hemiparesis
Physiotherapy plays a key role in the treatment of hemiparesis, as it can help improve strength, mobility, and overall function. The specific approach to physiotherapy will depend on the individual's symptoms, level of impairment, and overall health, but typically involves the following:
Assessment: The physiotherapist will assess the individual's strength, mobility, and overall function to identify specific areas of weakness or impairment.
Goal setting: Based on the assessment, the physiotherapist will work with the individual to set specific goals for their rehabilitation.
Exercise: Exercise is a key component of physiotherapy for hemiparesis. The physiotherapist will develop a customized exercise program that is tailored to the individual's needs and goals. This may involve exercises to help improve strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination.
Manual therapy: Manual therapy techniques, such as massage or joint mobilization, may be used to help improve mobility and reduce pain and stiffness.
Gait training: Gait training involves working on walking and mobility, and may involve the use of assistive devices, such as a walker or cane.
Functional training: Functional training involves practicing specific activities that the individual needs to perform in their daily life, such as getting dressed or cooking a meal.
Education: The physiotherapist will provide education on proper body mechanics, exercises, and strategies to help the individual manage their symptoms and improve their function.
The frequency and duration of physiotherapy will depend on the individual's specific needs and goals, but typically involves regular sessions over a period of weeks or months. It is important to work closely with a physiotherapist to ensure that the treatment plan is effective and appropriate for the individual's needs.
How to Prevent Hemiparesis?
The prevention of hemiparesis largely depends on identifying and addressing underlying risk factors or conditions that may increase the risk of developing the condition. Some strategies that may help prevent hemiparesis include:
- Managing high blood pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke, which can cause hemiparesis. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and/or medication may help reduce the risk of stroke and hemiparesis.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is another risk factor for stroke and hemiparesis. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise may help reduce the risk.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for stroke and other cardiovascular diseases, which can cause hemiparesis. Quitting smoking may help reduce the risk.
- Managing diabetes: Diabetes is a risk factor for stroke and cardiovascular disease, which can cause hemiparesis. Managing blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes and/or medication may help reduce the risk.
- Managing heart disease: Heart disease, such as atrial fibrillation or heart failure, can increase the risk of stroke and hemiparesis. Managing heart disease through lifestyle changes and/or medication may help reduce the risk.
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and manage underlying conditions that may increase the risk of hemiparesis.
While some risk factors for hemiparesis cannot be controlled, such as age or family history, taking steps to manage underlying conditions can help reduce the risk. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for preventing hemiparesis based on individual risk factors and medical history.
Conclusion
Hemiparesis is a condition characterized by weakness or paralysis on one side of the body. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including stroke, traumatic brain injury, and brain tumors. The symptoms of hemiparesis can be debilitating and can impact the individual's ability to perform daily activities.
The treatment of hemiparesis typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, medication, and other interventions to help improve mobility and function. The goal of treatment is to help the individual regain as much function as possible and improve their quality of life.
Prevention of hemiparesis largely depends on identifying and addressing underlying risk factors or conditions that may increase the risk of developing the condition. Strategies such as managing high blood pressure, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help reduce the risk.
Overall, hemiparesis can have a significant impact on an individual's physical and emotional well-being. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment and prevention plan that addresses the individual's specific needs and goals.
No comments:
Post a Comment